
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

The "Fuse of Transformer" plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical power systems. As the backbone of modern electrical infrastructure, transformers are essential for voltage regulation and energy distribution. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity demand is expected to grow by 30% by 2040, necessitating efficient and safe transformer operations. The integration of advanced fuse technologies can significantly enhance the operational integrity of transformers, protecting them from overcurrent and fault conditions that could lead to system failures.
In recent years, the demand for specific transformer types and their respective fuses has increased, driven by the growing need for renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies. The global transformer market is projected to reach USD 47.38 billion by 2027, as reported by Research and Markets, highlighting the importance of selecting the right fuse for each application. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of transformers, their functions, and how the appropriate fuse contributes to their efficiency and longevity, ultimately safeguarding electrical distribution networks against potential hazards and enhancing overall performance in the rapidly evolving energy landscape.
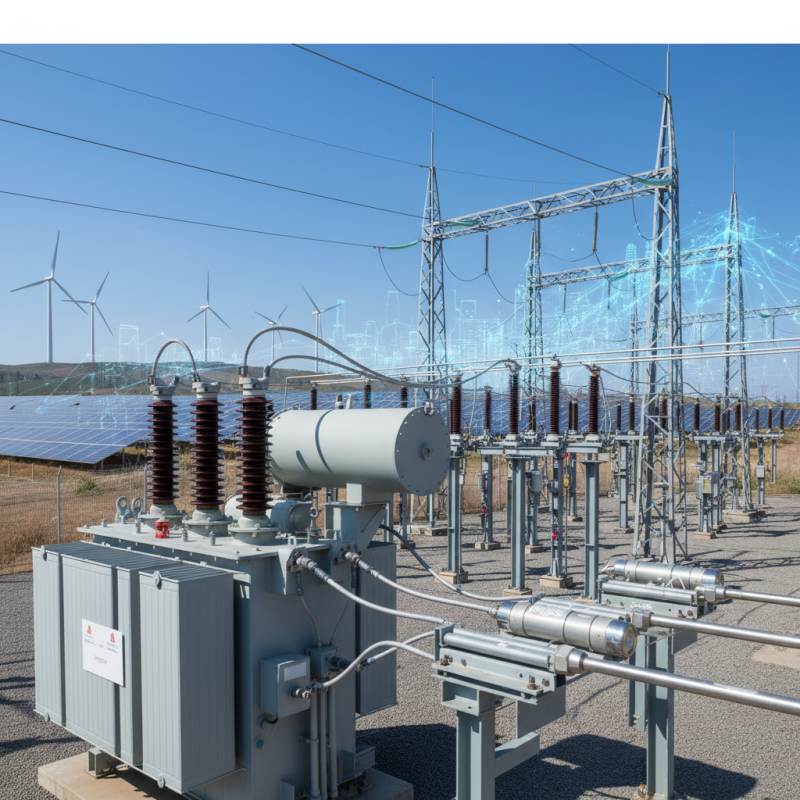


Transformers are essential electrical devices used to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. They play a critical role in power distribution and voltage regulation in various applications, from residential power supply to industrial machinery. Understanding the basics of transformers begins with their core components, which include the primary winding, secondary winding, and a magnetic core. These elements work together to either step up or step down voltages, making transformers versatile and indispensable in modern electrical systems.
There are several types of transformers designed for specific functions, including step-up transformers, which increase voltage levels, and step-down transformers, which decrease them. Additionally, isolation transformers are crucial for separating different sections of electrical systems to enhance safety and reduce noise. Other types, such as autotransformers and three-phase transformers, cater to specialized applications, ensuring efficiency in various sectors, including power generation, transmission, and distribution. Each type of transformer serves distinct operational needs, making a comprehensive understanding of their functions and applications vital for those working in electrical engineering and related fields.
Transformers play a crucial role in the functioning of electrical systems, serving as vital components that facilitate the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. Their primary function is to step up or step down voltage levels, which is essential for minimizing energy losses over long distances. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), approximately 10% of energy is lost during transmission due to resistance in the conductors. By using transformers to adjust voltage levels, these losses can be significantly reduced, making power distribution more efficient and cost-effective.
In addition to voltage regulation, transformers also provide electrical isolation between different parts of power systems. This isolation helps to protect sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and surges, enhancing overall system reliability. According to the IEEE Power and Energy Society, failures in electrical systems can lead to economic losses of billions of dollars annually, underscoring the importance of reliable transformer functionality. Moreover, modern smart grid technologies increasingly rely on transformers with advanced monitoring systems that allow for real-time data analysis, ensuring optimal performance and quick response to potential issues. This evolution illustrates the vital role transformers will continue to play in future electrical infrastructures, as they adapt to emerging technologies and increasing energy demands.
Transformers play a crucial role in electrical systems, facilitating the transfer of electrical energy between circuits while adjusting voltage levels according to application needs. Among the most common transformer types, the step-up transformer is designed to increase voltage, making it essential in power generation and transmission to minimize energy loss over long distances. Conversely, the step-down transformer reduces voltage, which is vital in distributing electricity to homes and businesses, ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
Another important type is the isolation transformer, which serves to decouple two circuits, providing safety by preventing potential hazardous voltages from affecting sensitive equipment. This is particularly useful in medical settings and for high-precision electronics. Additionally, autotransformers, which share a common winding for both primary and secondary sides, are commonly used in applications requiring voltage regulation, such as motor starters and test equipment. Each of these transformers is tailored to specific functions, making them indispensable in various industries ranging from utilities to consumer electronics.
When evaluating transformer types, understanding their functions and efficiency is essential for optimal application. Different transformer designs cater to varied needs, from step-up and step-down transformers used in power distribution to isolation transformers that enhance safety. Each type has unique operational characteristics and efficiencies that can significantly impact performance. A comparative analysis reveals that while traditional models may suffice for standard uses, modern designs often offer greater efficiency and compactness, driven by advancements in materials and technology.
Tips: When choosing a transformer, consider the specific load requirements and the operational environment. Ensure that the selected transformer not only meets the voltage and current specifications but also adheres to the necessary safety regulations.
Furthermore, efficiency is not merely about the energy loss in the form of heat but also involves factors like size, weight, and cost. More efficient transformers typically operate at lower temperatures and can lead to reduced long-term operational costs. The materials used in winding and core also play a crucial role, making it necessary to select designs that maximize performance while minimizing energy wastage.
Tips: Regular maintenance and monitoring of transformer performance can significantly prolong its lifespan and efficiency. Implementing predictive maintenance techniques can prevent unexpected downtimes and sustain optimal operational capabilities.
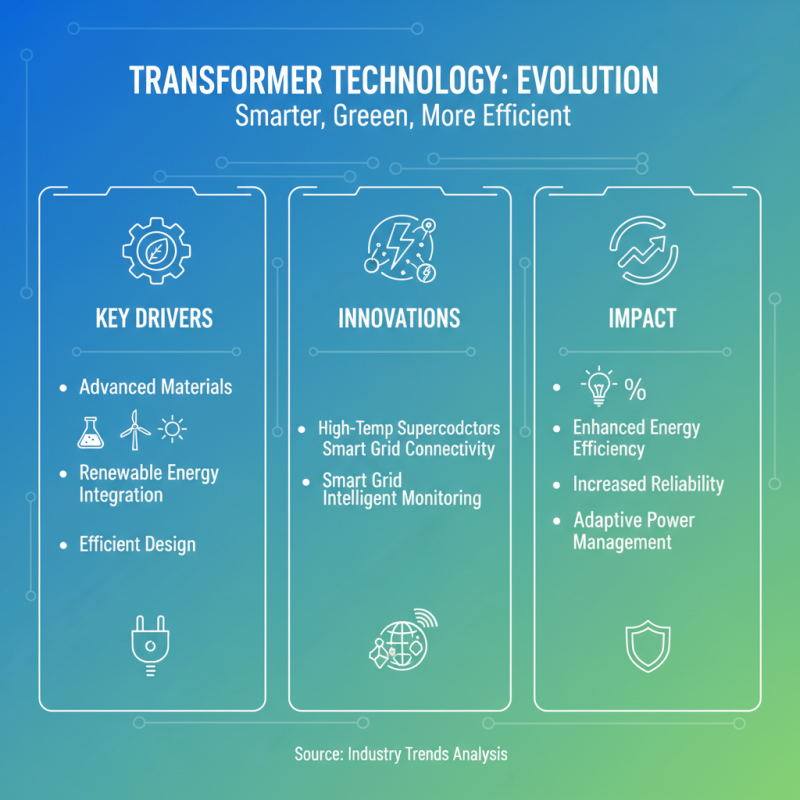
The landscape of transformer technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in materials, design, and renewable energy integration. With the increasing demand for efficient energy solutions, innovations such as high-temperature superconductors and smart grid connectivity are set to redefine how transformers function in both industrial and residential applications. These trends indicate a move towards more intelligent systems that can monitor performance and adapt to varying power demands, ultimately enhancing energy efficiency and reliability.
Tips: When considering the future of transformer technology, always keep an eye out for emerging technologies such as digital sensors and IoT integration. These can significantly improve operational monitoring and offer predictive maintenance capabilities, enabling users to optimize performance and reduce downtime.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in transformer design. The focus on eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient systems will not only help reduce the carbon footprint but also lead to innovations in recycling and lifespan extension of transformers. As industries pivot towards greener practices, transformers are expected to play a vital role in facilitating the transition to renewable energy sources, making them an essential component of future energy infrastructures.
Tips: For those interested in incorporating cutting-edge transformer technology, consider investing in systems that prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability. This not only benefits the environment but can also lead to cost savings in operation and maintenance over time.





