-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Choosing the right Surge Arrester can be a daunting task. The increasing reliance on electronic devices makes understanding surge protection essential. According to a report by the Electric Power Research Institute, electrical surges can cause billions in damages annually. A suitable Surge Arrester acts as a critical line of defense.
Many consumers underestimate the importance of this device. For instance, a single lightning strike can generate high-voltage surges. This can lead to equipment failure or costly repairs. Industry experts suggest assessing your specific needs, which often remain overlooked. The market offers various types of Surge Arresters, each designed for particular applications.
Selecting the right product should not be based solely on price. Quality and specifications also matter significantly. Unfortunately, some buyers may regret choices made under pressure. Reflecting on this can lead to better decisions. Ultimately, understanding surge protectors will provide better security for your electronics.

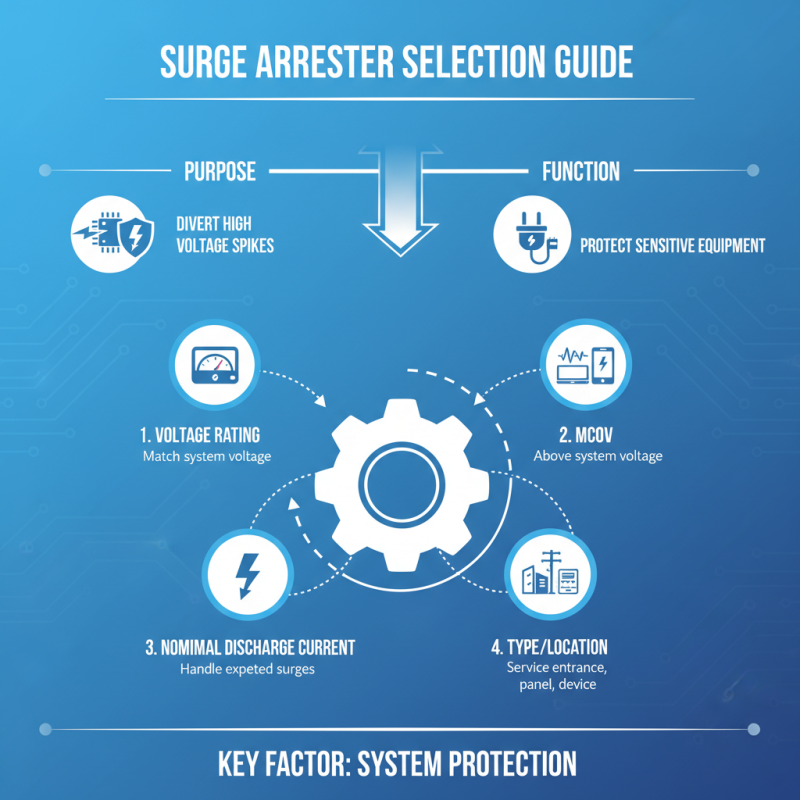
Selecting the right surge arrester is crucial for protecting electrical systems. A surge arrester's main purpose is to divert high voltage spikes away from sensitive equipment. There are several factors to consider when choosing an appropriate type.
First, it is essential to determine the voltage ratings. Different systems operate at varying voltage levels. For example, low-voltage systems usually require 120-600 V surge arresters. In contrast, medium-voltage levels often range from 1 kV to 36 kV. Choosing the wrong rating could lead to equipment failure. According to a recent industry report, improper ratings account for nearly 30% of surge-related damage.
Secondly, assess the environmental conditions. Surge arresters are affected by temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. For example, outdoor installations may need arresters rated for harsher conditions. A study revealed that arresters installed in challenging environments can have a 50% shorter lifespan if not properly selected. Evaluating these factors helps ensure equipment durability and reliability.
Another critical aspect is the type of surge protection technology. Options include Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) and Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs). Each has its benefits and drawbacks. MOVs can provide fast response times, but they may degrade over time. GDTs, on the other hand, often have higher surge capacity. Understanding these technologies leads to better decision-making.
When selecting a surge arrester, understanding the surge ratings is crucial. Surge protection devices are rated in kilovolts (kV). This rating indicates the maximum voltage the device can handle during a surge. For example, a 10 kV surge arrester is typically suitable for medium voltage systems. However, real-world applications require careful consideration of potential surge environments.
The right choice depends on your specific needs. High-voltage systems may need devices rated at 20 kV or more. On the other hand, lower-voltage applications can often utilize devices rated at 5 kV. It's essential to assess your electrical system's requirements and the types of surges it may encounter. A standardized surge event, like a lightning strike, can produce voltage spikes reaching several hundred kV.
**Tip:** Regularly Test Your Equipment. Routine checks can uncover weaknesses in your surge protection strategy.
Experts suggest that assessing the location of your setup is equally important. Some areas are more prone to electrical surges from weather conditions or industrial activities. You might think you need a high rating, but sometimes a lower-rated arrester suffices.
**Tip:** Stay Informed About Local Conditions. Knowledge of your environment can significantly impact your choices.
This chart illustrates the surge ratings of different types of surge arresters used for various applications. The ratings are measured in kilovolts (kV), categorizing the devices by their maximum voltage withstand capabilities.
Choosing the right surge arrester involves evaluating its energy absorption capacity. This is critical for optimal protection against voltage spikes. Energy absorption capacity is often rated in joules. A higher rating typically indicates better protection.
Many industry reports suggest a surge arrester should have an absorption capacity of at least 20,000 joules for residential applications. However, this could vary based on specific electrical setups. For data centers or industrial applications, the requirement may exceed 50,000 joules. It's important to assess your electrical load carefully.
Misestimations can lead to inadequate protection. Take time to analyze your system's voltage characteristics. Sometimes, overly ambitious ratings can mislead users. Simpler designs might provide sufficient protection with lower capacity ratings. Understanding your unique needs ensures you choose appropriately.
| Surge Arrester Type | Energy Absorption Capacity (kJ) | Voltage Rating (kV) | Installation Location | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 30 | 10 | Outdoor | Telecommunications, Renewable Energy |
| Type 2 | 50 | 15 | Indoor | Industrial Equipment, Data Centers |
| Type 3 | 75 | 20 | Outdoor & Indoor | Utilities, Commercial Buildings |
| Type 4 | 100 | 25 | Indoor | Critical Infrastructure, Large Scale Industries |
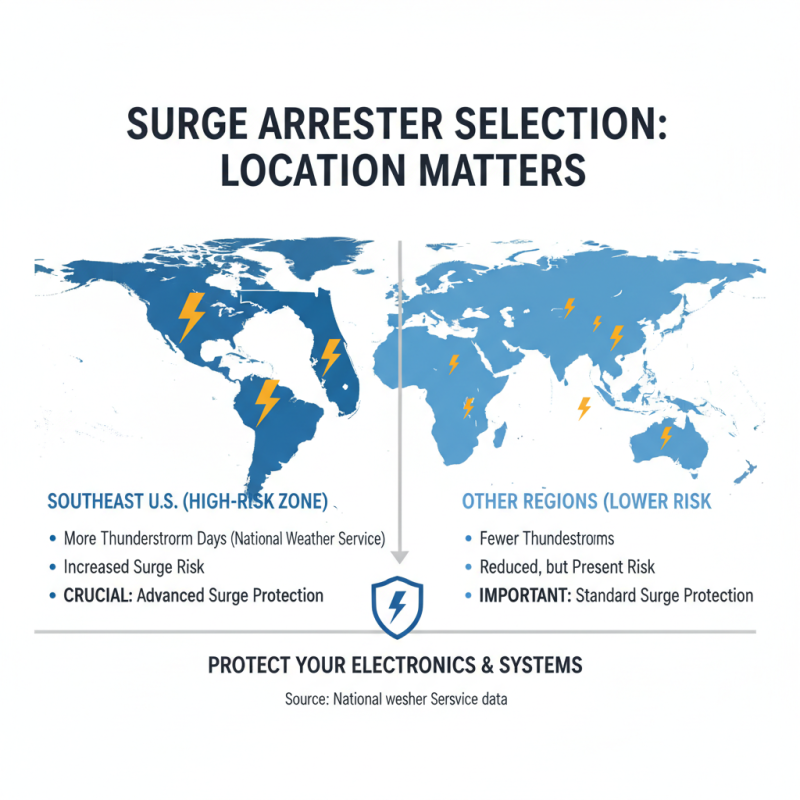
When selecting a surge arrester, location plays a critical role. Certain regions are more prone to electrical storms. For instance, the National Weather Service reports that states in the Southeast experience more thunderstorm days each year than other areas. This increases the risk of surge events, making the selection of a surge arrester even more crucial.
A surge arrester's efficiency can depend heavily on its installation environment. For urban areas with dense construction, the risk of voltage spikes is higher due to nearby electric systems. According to a report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE), urban environments can experience surge events over 20% more frequently than rural settings. Conversely, rural areas might have different requirements. Here, the emphasis could be on protecting against induced surges from nearby lightning strikes.
The appropriate surge arrester should match local risks. An arrester suitable for a storm-prone area may not be as effective in milder climates. Understanding the common risks of your specific location can inform better choices. Insufficient attention to these factors can lead to inadequate protection. This necessitates careful assessment rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
When selecting a surge arrester, compliance with industry standards is crucial. Many standards guide the design and testing of these devices. Knowing which ones apply to your situation helps ensure safety and effectiveness. Look for certifications from recognized organizations. They confirm that the surge arrester meets essential performance criteria.
It's important to consider local regulations, too. Different regions may have specific requirements. Not all surge arresters will comply everywhere. This may lead to unexpected failures during operation. Consulting industry guidelines can prevent this issue.
Thinking through the safety implications is vital. A non-compliant device can pose hazards to both equipment and personnel. A surge arrester that does not meet standards might not perform during a surge event. This could result in costly damage. Investing time in research guarantees that you are choosing a product that safeguards your systems adequately.