-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Choosing the right High Voltage Fuse can significantly impact equipment safety and efficiency. A report by the International Electrotechnical Commission shows that improperly selected fuses account for 30% of electrical failures. This staggering statistic underscores the importance of this decision-making process.
Expert James Thornton, a leading figure in the high voltage industry, once remarked, "An adequate High Voltage Fuse is crucial to preventing catastrophic breakdowns." His insight highlights the need for thorough knowledge of specifications and ratings. Each application has unique demands.
Look for key attributes like current rating, voltage rating, and breaking capacity. Often, businesses overlook these criteria. This oversight can lead to unnecessary risks. Appropriate selection requires careful consideration of both technical aspects and operational needs. It is a critical task that can shape the reliability of electrical systems.

High voltage fuses play a crucial role in electrical systems. Their primary function is to protect equipment from overloads and short circuits. These fuses effectively interrupt current flow when dangerous levels are detected. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), proper fuse selection helps reduce equipment failure significantly.
When choosing a high voltage fuse, several factors should be considered. Voltage rating is one of the most critical. It must align with your system's operational voltage to ensure safety. Another key aspect is the fuse's interrupting capacity. A fuse with inadequate interrupting capacity can fail to protect your equipment. Data from industry reports indicate that fuse failures can lead to significant downtime and repair costs.
Tips: Always consult technical specifications before making a decision. If uncertain, seek expert advice. Consider the environment where the fuse will be installed. High temperatures or humidity levels can affect fuse performance.
Selecting the right fuse requires deep understanding. Many users often overlook the current rating. It is essential to assess the load characteristics accurately. Underestimating load can lead to fuses blowing more frequently. Conversely, overrating can cause delayed protection. This fine balance is essential for a reliable high voltage system.

Choosing the right high voltage fuse is crucial for effective electrical protection. When selecting a fuse, consider voltage rating, current rating, and interruption capacity. A fuse must match the specific voltage requirements of your system. Look for fuses rated for at least the system voltage.
Current ratings are equally important. A fuse must carry the normal operating current without blowing. However, if it's too high, it won’t protect your equipment. This balance can be challenging.
**Tips:** Always check the manufacturer specifications. Use a multimeter to assess current flows before installation.
Interruption capacity indicates how much fault current a fuse can safely interrupt. Ensure this capacity exceeds your system's maximum possible fault current. Selecting a fuse with insufficient capacity can lead to catastrophic failures.
**Tips:** Consult a professional for installation. Small miscalculations can lead to significant issues. Regularly inspect fuses for wear and damage, as deteriorating fuses can fail unexpectedly.
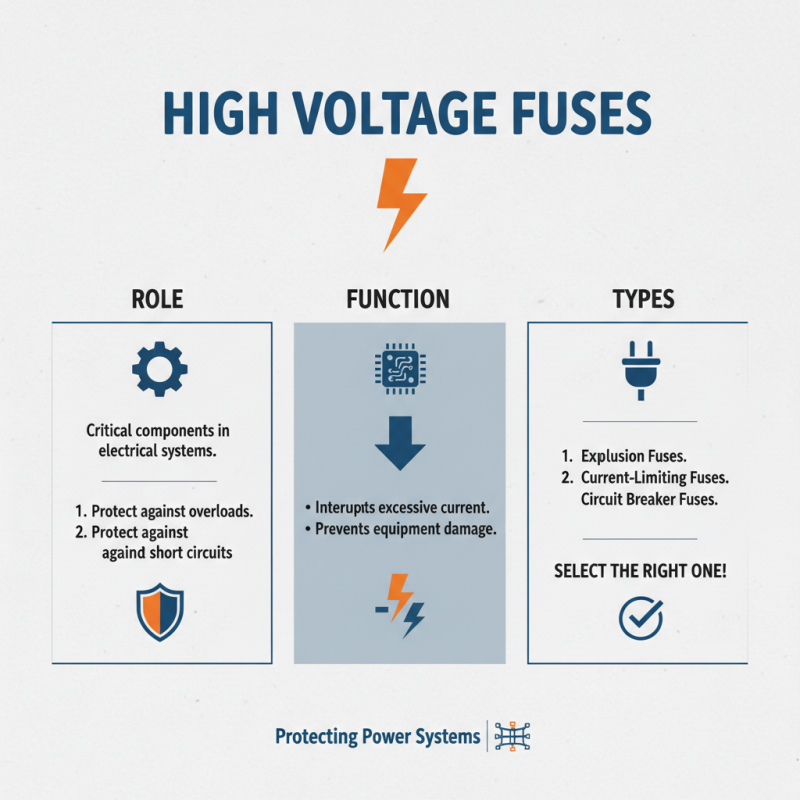
High voltage fuses are critical components in electrical systems. They protect against overloads and short circuits. Understanding the types of high voltage fuses is essential for selecting the right one.
There are several types of high voltage fuses available. Expulsion type fuses are common in outdoor applications. They work by expelling the melting element, which eliminates the fault current quickly. A report from the Electrical Safety Foundation indicates that these fuses are effective in reducing risk. Another type is the current-limiting fuse. It minimizes damage during a fault by interrupting the current flow sooner. The average operating voltage for these fuses can reach up to 36kV.
Applications vary widely. Utilities often use high voltage fuses in substations. In industrial setups, they protect machinery. However, some fuses have a limited interruption capacity. This might lead to equipment damage. A recent study identified that nearly 15% of fuse failures are due to inappropriate selection. Choosing the right type based on the application is crucial.
When selecting a high voltage fuse, understanding voltage and current ratings is crucial. These ratings dictate how well the fuse will perform in specific applications. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) states that fuses should match the maximum voltage present in the circuit. For instance, a fuse rated for 1,000 volts should be used in systems operating below this threshold.
Current ratings are equally important. A fuse must handle normal operating currents. If the current rating is too low, the fuse will blow frequently. Conversely, if rated too high, it may not provide adequate protection. Data from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) suggests that around 60% of equipment failures are linked to improper fuse applications.
Many users overlook environmental factors. High temperatures can cause fuses to operate below their ratings. At the same time, the application location can influence the fuse performance. It might seem simpler to select fuses based solely on ratings, but real-world conditions significantly impact reliability. Reflect on specific needs. Understanding these ratings leads to better choices and ensures safety in high voltage applications.
| Voltage Rating (kV) | Current Rating (A) | Fusible Element Material | Breaking Capacity (kA) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 100 | Copper | 25 | Transformers |
| 25 | 200 | Aluminum | 31 | Switchgear |
| 36 | 400 | Silver | 50 | Generators |
| 52 | 600 | Copper | 63 | Industrial Equipment |
Installing and maintaining high voltage fuses requires careful attention. Before installation, ensure the area is safe and well-lit. Inspect the fuse for any visible damage. Clean the installation site and use appropriate tools. Wear safety gear, including gloves and goggles. Secure fuses tightly but avoid excessive force, which may damage them.
Maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Regular inspections help catch potential issues early. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating. If fuses blow frequently, it might indicate an underlying problem. Consider environmental factors too; moisture and dust can affect performance.
Documentation is often overlooked. Keep a log of installations and any maintenance performed. This record helps in evaluating performance over time. Be open to reevaluating your choices; the best fuse for your needs may change as technology advances or conditions vary. High voltage fuses play a significant role, so regular care is non-negotiable.