-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Choosing the right ceramic fuse for your electrical applications is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the safety and efficiency of your operations. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), improper selection of protective devices, including ceramic fuses, contributes to a staggering 15% of electrical failures in industrial settings. This underscores the necessity for thorough understanding and consideration when selecting fuses to safeguard against potential overloads and short circuits.
Renowned industry expert, Dr. Emily Carter, asserts, "The reliability of your electrical system hinges on the choice of protective devices. Ceramic fuses, with their excellent material properties, provide durability and high interrupting capacity, essential for modern electrical applications." Dr. Carter's insights highlight the importance of considering the specific requirements of each application, as well as the unique advantages ceramic fuses offer, such as their ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosion, making them ideal for various industrial and commercial environments.
As the demand for efficient and reliable electrical systems continues to rise, understanding the criteria for selecting the right ceramic fuse becomes increasingly vital. This guide aims to equip you with essential knowledge and best practices to ensure that your choice aligns with industry standards and effectively meets your operational needs.

Ceramic fuses play a crucial role in electrical systems by providing reliable protection against overcurrent conditions. Unlike traditional fuses, which may be made from glass or other materials, ceramic fuses are constructed from durable ceramic materials that can withstand high temperatures and are less prone to breaking under stress. This robustness is vital in applications where durability and reliability are essential, as it helps maintain the integrity of the electrical system, prolonging the lifespan of connected components.
The functionality of ceramic fuses revolves around their ability to interrupt the flow of electrical current when it exceeds a specified limit. When an overcurrent occurs, the fuse element inside the ceramic body melts, effectively breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring and connected devices. This quick response helps mitigate the risks of electrical fires and equipment failure. Additionally, ceramic fuses can have varying time-delay characteristics, allowing for brief surges in current without sacrificing protection, making them suitable for diverse applications from industrial machinery to household electrical systems. Understanding how these fuses operate and the environments they are suited for is key to selecting the right fuse for specific electrical applications.
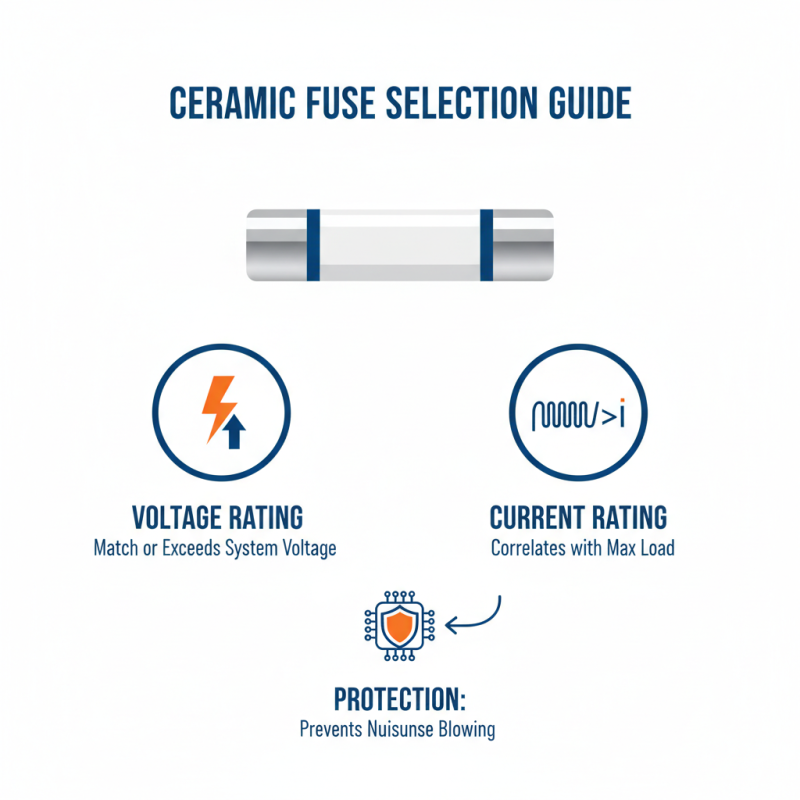
When selecting a ceramic fuse for electrical applications, understanding the specific electrical requirements is crucial. First, consider the voltage and current ratings of your application. The voltage rating of the fuse must match or exceed the system voltage to ensure safe operation, while the current rating should correlate with the maximum load to prevent nuisance blowing. It's important to have a fuse that will adequately protect the circuit without failing under normal operating conditions.
Additionally, assess the type of load the fuse will protect. Different applications may involve resistive, inductive, or capacitive loads, each of which can influence the choice of fuse. For instance, inductive loads typically require a fuse that can handle a higher inrush current, which is a surge occurring when the device is first energized. Understanding the electrical characteristics of your specific application will aid in selecting a fuse that offers reliable protection while accommodating operational demands.
When selecting the right ceramic fuse for your electrical applications, several key considerations must guide your decision-making process. First and foremost, understanding the operational environment is crucial. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and installation location can significantly impact a fuse’s performance. For instance, extreme temperatures may affect the thermal characteristics of the fuse, necessitating a selection that can withstand these conditions without compromising reliability.
Another important consideration is the fuse rating, which includes both voltage and current ratings. The voltage rating must be compatible with the circuit in which the fuse will be used to ensure safety and effectiveness. The current rating should reflect the maximum expected load while allowing for inrush currents typical in certain applications. Additionally, consider the time-delay characteristics of the fuse; a slow-blow fuse may be preferable for applications with temporary overloads, while fast-acting fuses are better suited for sensitive electronics.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a ceramic fuse that will provide optimal protection for your electrical systems.
When selecting ceramic fuses for electrical applications, evaluating quality and safety standards is paramount.
Ceramic fuses are known for their excellent insulating properties and high temperature resistance, which makes them suitable for a variety of electrical circuits. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard IEC 60269, ceramic fuses must undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and safety during operation. Understanding these standards can help in identifying products that not only meet but exceed the required safety measures.
Tip: Always check for compliance with regional and international safety standards when choosing a ceramic fuse. Look for certifications from recognized bodies, which can give you confidence in the product’s quality.
Moreover, recent industry reports indicate that improper fuse selection can lead to circuit failures and potential fire hazards. For instance, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has noted a significant percentage of electrical fires caused by faulty fuse installations. Selecting fuses that have undergone comprehensive testing for their breaking capacity and temperature ratings can mitigate these risks.
Tip: Maintain an updated log of all installed fuses and their specifications to facilitate regular inspections and ensure that they meet the evolving safety standards.
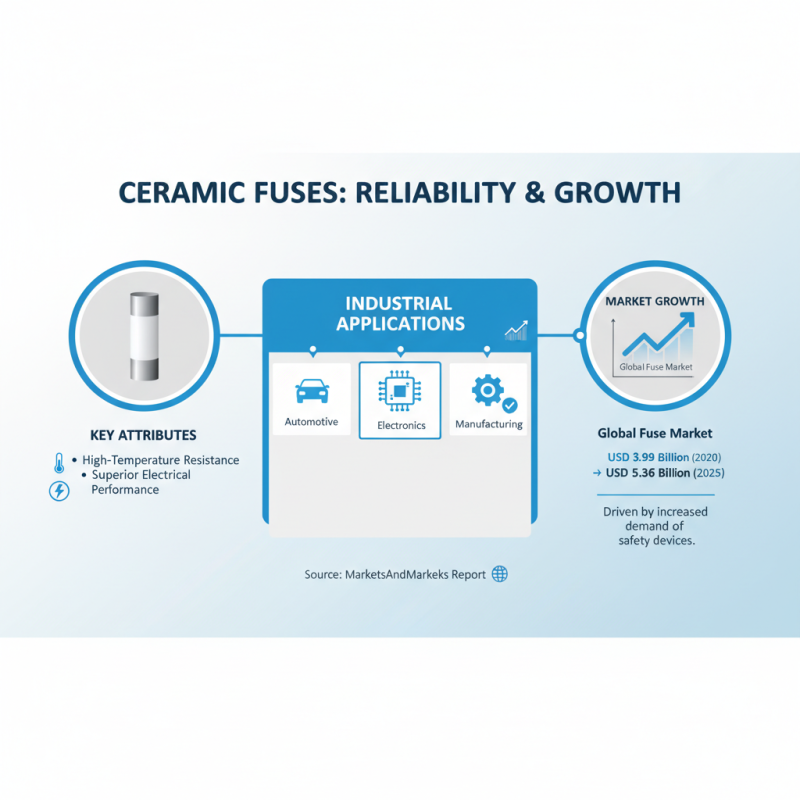
Ceramic fuses are increasingly recognized for their reliability and efficiency in various industrial applications. In sectors such as automotive, electronics, and manufacturing, these fuses provide vital protection for circuits. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global fuse market is projected to grow from USD 3.99 billion in 2020 to USD 5.36 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for safety devices in electrical and electronic equipment. This growth underscores the integral role of ceramic fuses, which are known for their high-temperature resistance and superior electrical performance under challenging conditions.
In the automotive industry, ceramic fuses are commonly used in both conventional and electric vehicles, safeguarding sensitive electronic components by interrupting excessive current flow. They are favored for their ability to handle high inrush currents, which is crucial for components like motor starters and battery management systems. Moreover, in the electronics sector, ceramic fuses play a significant role in industrial automation and consumer appliances, where their compact size and robust design offer effective overcurrent protection. A study by Transparency Market Research highlights that the demand for ceramic fuses in electronics applications is anticipated to rise by approximately 30% over the next five years, driven by advancements in smart technology and increasing safety regulations.