-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the realm of electrical systems, the importance of safety and protection against overloads cannot be overstated. One critical component that plays a vital role in safeguarding electrical circuits is the Low Voltage Fuse. Designed specifically to protect low voltage equipment from excessive currents, these fuses act as guardians, interrupting the circuit when current flow exceeds safe levels. Understanding how a Low Voltage Fuse operates is essential for both professionals in the field and everyday users of electrical appliances, as it ensures the reliability and longevity of electrical systems.
Low Voltage Fuses come in various types and specifications, tailored to meet the diverse needs of different electrical applications. They are integral to ensuring that devices operate efficiently without the risk of damage from short circuits or overloads. By acting quickly to disconnect the power supply when a fault occurs, Low Voltage Fuses minimize the potential for fire hazards and equipment failures. In this article, we will explore the function, advantages, and types of Low Voltage Fuses, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in electrical systems and guiding users in making informed decisions for their safety and equipment protection.

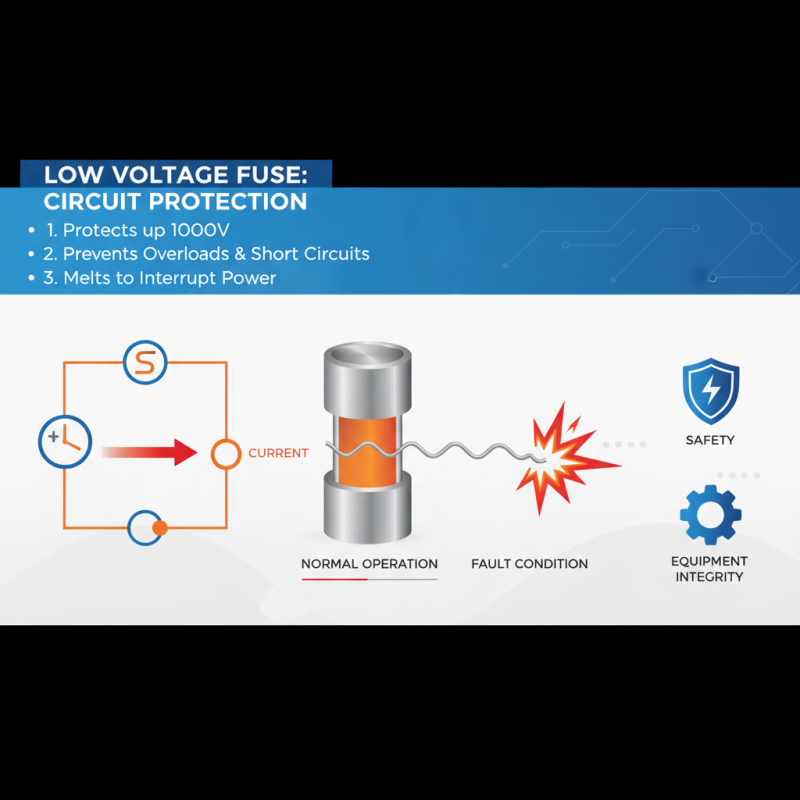
A low voltage fuse is a crucial component in electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. Operating typically at voltages up to 1,000 volts, these fuses are essential for maintaining the safety and integrity of electrical installations. When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds its rated capacity, the fuse element melts, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing potential damage to connected devices.
In addition to their protective function, low voltage fuses are also employed to ensure the reliability of electrical systems. They come in various sizes and ratings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential wiring to industrial machinery. Low voltage fuses help to minimize the risk of electrical fires and equipment failures by offering a straightforward and effective method for circuit protection. When a circuit needs to be restored after a fuse blows, replacing the fuse allows for quick recovery without complicated repairs, highlighting their integral role in everyday electrical safety.
Low voltage fuses play a critical role in protecting electrical systems from overcurrent situations. They function by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds a specified limit, preventing damage to equipment and reducing the risk of fire. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), low voltage fuses can effectively handle fault currents up to 10 times their rated current for a limited duration, ensuring the system's integrity is maintained even under stress. This capability is crucial in industrial settings where unplanned outages can lead to significant operational losses.
Another key function of low voltage fuses is their ability to provide selective coordination in electrical networks. This means that, when a fault occurs, the fuse closest to the fault will blow while allowing downstream devices to continue functioning. A study published in the Journal of Electrical Engineering highlights that implementing selective coordination can enhance system reliability by 30%, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity. Fuses also come in various ratings and forms, allowing engineers to tailor their solutions to specific application needs, whether in residential, commercial, or industrial environments. By using low voltage fuses strategically, electrical systems can achieve a safer and more efficient operation.
Low voltage fuses play a critical role in protecting electrical systems from overcurrent situations, ensuring safety and efficiency throughout various applications. These fuses are categorized into several types, each suited for specific uses in different environments. Among the most common types are cartridge fuses, plug fuses, and resettable fuses, which are used to safeguard electrical circuits in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global low voltage fuse market is projected to grow significantly, reflecting the increasing demand for reliable protection devices in the face of rising electrical system complexities.
Cartridge fuses, known for their cylindrical shape, are widely used in industrial applications due to their high interrupting capacity. These fuses can handle large currents and are designed to operate effectively in high-demand environments. On the other hand, plug fuses are more common in residential settings, offering a convenient way to replace blown fuses quickly. Resettable fuses, or PTCs, provide an additional advantage as they can automatically reset after a fault condition is cleared. A study by Research and Markets revealed that the inclusion of smart technologies in fuse design is becoming more prevalent, enhancing their functionality and integration with modern electrical systems, which further underscores the diverse applications of low voltage fuses across various sectors.
| Fuse Type | Current Rating (A) | Voltage Rating (V) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Cartridge Fuse | 1 - 32 | 250 | General electrical circuits, appliances |
| Glass Fuse | 0.5 - 30 | 250 | Automotive, lighting systems |
| Resettable Fuse (PTC) | 0.1 - 10 | 60 | Computer peripherals, consumer electronics |
| Fusible Links | 10 - 40 | 600 | HVAC systems, industrial machinery |
| Blade Fuse | 5 - 30 | 32 | Automotive applications, power distribution |
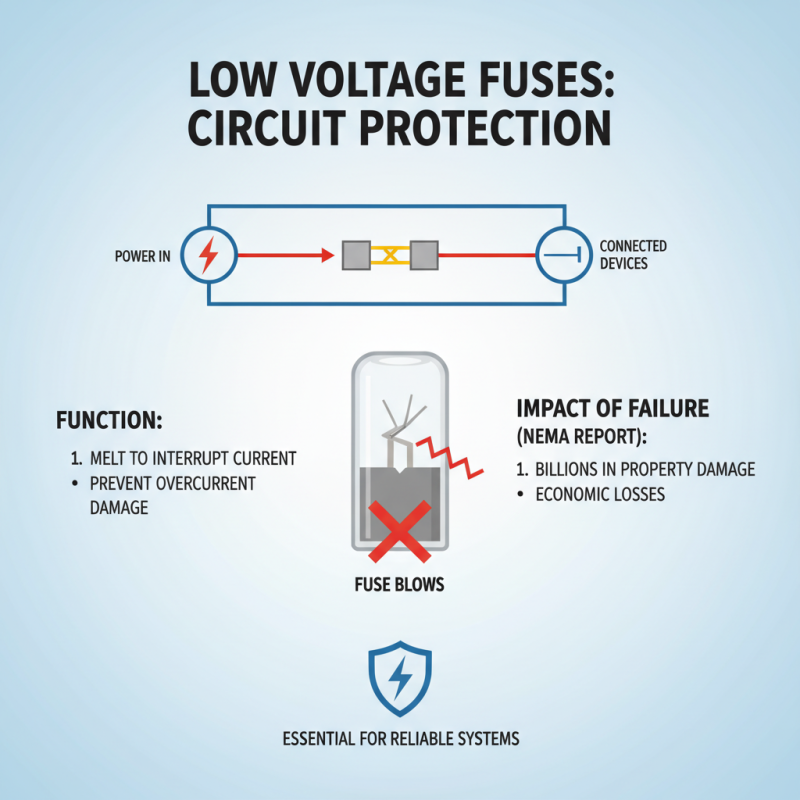
Low voltage fuses are critical components in electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overcurrent conditions. These fuses work by melting a conductive element when the electrical current exceeds a specified threshold, thus interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing potential damage to the wiring and connected devices. According to a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), improper protection can result in significant economic losses, with electrical failures accounting for billions in property damage each year. This underscores the importance of effectively integrating low voltage fuses into circuit designs.
To further elucidate how low voltage fuses protect electrical circuits, it's essential to recognize their role as the first line of defense against overloads and short circuits. By ensuring that current levels remain within safe limits, these fuses enhance overall system reliability and efficiency. For instance, industry data suggests that circuits with adequate fuse protection experience up to 30% longer service life compared to those without. This not only improves safety but also reduces maintenance costs associated with circuit repairs.
Tips: Always select a fuse with the appropriate rating for your circuit's specific requirements. Regularly inspecting fuses can prevent unexpected failures and extend the lifespan of your electrical systems. Additionally, consider employing a fuse monitoring system to proactively manage and replace fuses before they fail.
Low voltage fuses are essential components in electrical systems, acting as protective devices to prevent overloads and short circuits. When it comes to the installation and maintenance of these fuses, following established guidelines is crucial. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), proper installation includes ensuring fuses are rated for the specific amperage and voltage of the circuit they are protecting. Failure to comply can lead to inadequate protection and potential electrical failures.
During installation, positioning the fuse in an accessible location is advisable, facilitating easy replacement when necessary. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear or damage, as suggested by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Fuses should be replaced immediately if they show discoloration, which may indicate overheating, and a routine maintenance schedule can help in identifying issues before they escalate.
**Tip:** Always disconnect power before replacing a fuse. This simple step ensures safety during maintenance and reduces the risk of accidental harm from electrical surges.
Maintenance also involves keeping the surrounding area clean and free of dust or debris that could affect performance. Regular checks of the terminals can prevent oxidation build-up, which could lead to increased resistance and, subsequently, fuse failure. Implementing these practices will not only prolong the life of low voltage fuses but also enhance the overall reliability of electrical systems.
This bar chart displays the current ratings of common low voltage fuses used in electrical systems. The data reflects typical ratings in amperes for various applications.