-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the realm of electrical engineering, ensuring safety and efficiency is paramount, particularly when it comes to fuse protection. The DIN Standard Fuse, a crucial component in electrical circuits, plays a significant role in preventing excess current, safeguarding both equipment and users. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), proper fuse ratings can reduce the risk of electrical fires by up to 70%, underscoring their importance in maintaining operational integrity.
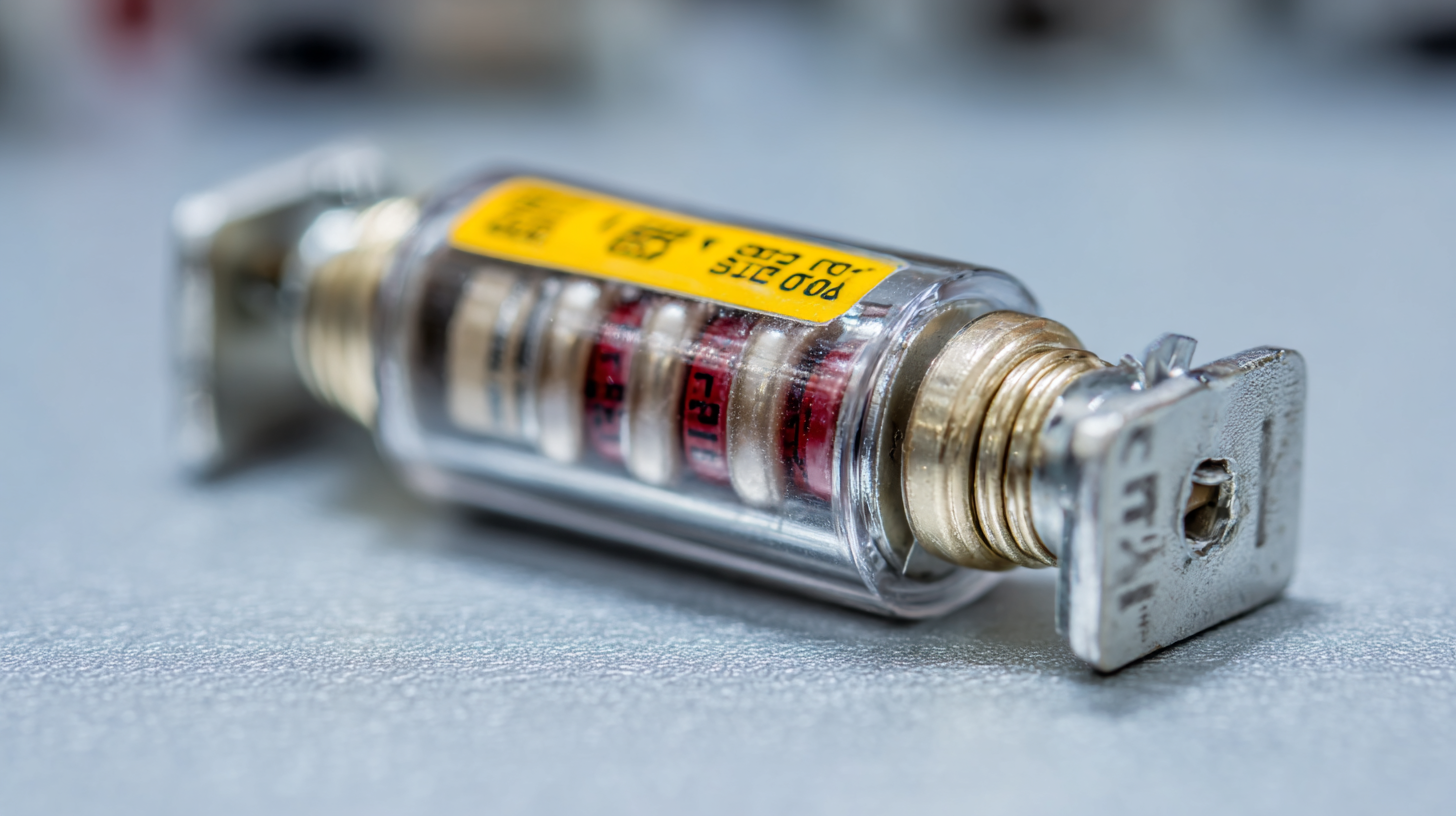

Furthermore, a report from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) highlights that electrical failures account for over 21,000 reported fires annually in the United States, many of which could be prevented through the use of appropriately rated DIN Standard Fuses. Understanding the nuances of these ratings is essential for engineers and technicians, as it directly impacts the reliability and safety of electrical installations in various applications.
When it comes to electrical safety, understanding DIN standard fuse ratings is crucial. DIN standards ensure that fuses meet specific safety and performance criteria, significantly minimizing the risk of electrical failures and hazards. Properly rated fuses can help to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, preventing potential fires and equipment damage. By adhering to these standards, electricians and engineers can offer greater reliability and peace of mind in their electrical installations.
**Tips:** Always check that the fuse ratings you are using correspond to the specific requirements of your electrical system. It’s essential to select fuses not only based on their voltage and current ratings but also on their breaking capacity, which indicates the maximum fault current they can safely interrupt.
Moreover, regular maintenance and inspection of fuses according to DIN standards can enhance system efficiency. Any signs of damage or wear should prompt immediate replacement to maintain safe operational conditions. Keeping documentation of fuse ratings and specifications can also aid in troubleshooting and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
This chart illustrates various DIN standard fuse ratings in amps, highlighting their significance in ensuring electrical safety and efficiency. Properly rated fuses help in protecting electrical circuits from overloads and potential hazards.
Choosing the right DIN standard fuse for your application is crucial to ensuring both electrical safety and operational efficiency. DIN fuses, which conform to the Deutsches Institut für Normung (German Institute for Standardization) standards, are designed to provide reliable protection against overcurrent situations. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), improper fuse ratings account for approximately 30% of electrical failures in industrial setups. This highlights the necessity for accurate selection based on load requirements, ambient temperature conditions, and installation environment.
When selecting DIN fuses, one must consider the specific current ratings that align with the equipment's operational load. For instance, the fuse must be rated slightly above the normal operating current to prevent nuisance blowing while still providing adequate protection against overloads. Industry standards indicate that using fuses with a rated current considerably above the required load can result in catastrophic failure, with potential damage costs reaching up to 20% of operational budgets. Moreover, factors like breaking capacity and responsiveness to fault conditions should also guide your choice. Conducting a comprehensive assessment of these parameters ensures that the selected fuse not only safeguards equipment but also enhances system efficiency.
When evaluating fuse ratings, it is crucial to understand the key parameters: amperage, voltage, and breaking capacity. Amperage refers to the maximum current a fuse can carry before it needs to interrupt the circuit. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), using fuses with a mismatch in amperage rating can lead to circuit overload, potentially causing damage to connected appliances or, worse, electrical fires. For instance, a report from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) indicated that improper rating of fuses contributed to over 25% of electrical fires in residential buildings from 2014 to 2018.
Voltage rating, on the other hand, signifies the maximum voltage a fuse can handle without failing. Utilizing a fuse rated for lower voltage in high-voltage applications can lead to catastrophic failures. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) emphasizes the importance of matching voltage ratings, stating that electric arcs can occur if a fuse is rated inadequately for the circuit voltage. Additionally, breaking capacity defines the maximum fault current a fuse can safely interrupt without failing. The Fuse Association highlights that selecting a fuse with appropriate breaking capacity is vital for preventing equipment damage and ensuring the safety of electrical systems. This understanding is essential in maintaining both efficiency and safety in electrical installations.
When selecting fuses for electrical systems, one common mistake is underestimating the importance of choosing the correct rating. Many users opt for a fuse based on convenience or availability rather than the specific requirements of their application. This can lead to inadequate protection, resulting in overcurrent situations that could damage equipment or create fire hazards. It is essential to understand the load that the fuse will be protecting and ensure that the selected fuse rating aligns with both the operational current and the potential surge conditions.

Another frequent oversight is neglecting the fuse characteristics, such as the time-current curve. Users often fail to recognize that different fuses react differently to overload conditions, with some designed for fast response and others for delayed action. Choosing the wrong type can result in nuisance blowing or insufficient protection. To avoid these pitfalls, thorough evaluation of the electrical circuit and a review of the manufacturer's specifications are crucial steps in the fuse selection process.
This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also improves overall efficiency in the electrical system.
Maintaining electrical systems for optimal efficiency and safety is crucial in today’s increasingly electrified environments. Regular inspections and timely upgrades can significantly reduce the risk of electrical failures. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures account for about 10% of all home structure fires in the United States, emphasizing the importance of diligent maintenance. Ensuring that electrical components are rated appropriately according to DIN standards can mitigate risks associated with overloads and short circuits, ultimately extending the lifespan of the system.

In addition to adhering to industry standards, implementing routine preventative maintenance techniques can lead to improved energy efficiency. The Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) reports that proper maintenance can enhance system efficiency by up to 20% in commercial settings. Simple practices such as tightening connections, cleaning panel boxes, and monitoring equipment loads can help prevent energy losses. Furthermore, utilizing advanced monitoring systems can provide real-time data on power consumption, allowing facilities to make proactive adjustments that not only enhance safety but also reduce energy costs. By prioritizing these maintenance tips, businesses and homeowners can ensure their electrical systems operate efficiently and safely.