-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, the demand for innovative materials that can withstand varying environmental conditions while providing reliable performance has never been greater. One such material that has gained significant attention is the Silicone Rubber Insulator. Renowned for its exceptional electrical insulating properties, flexibility, and resilience, Silicone Rubber Insulators are integral components in numerous modern applications ranging from electrical engineering to automotive and aerospace industries. This article delves into the diverse uses and benefits of Silicone Rubber Insulators, showcasing their ability to enhance performance, improve safety, and contribute to the overall efficiency of devices and systems. By exploring the versatility of these insulators, we aim to highlight their pivotal role in supporting the advancement of cutting-edge technologies, ultimately transforming the way we approach design and manufacturing in various sectors.
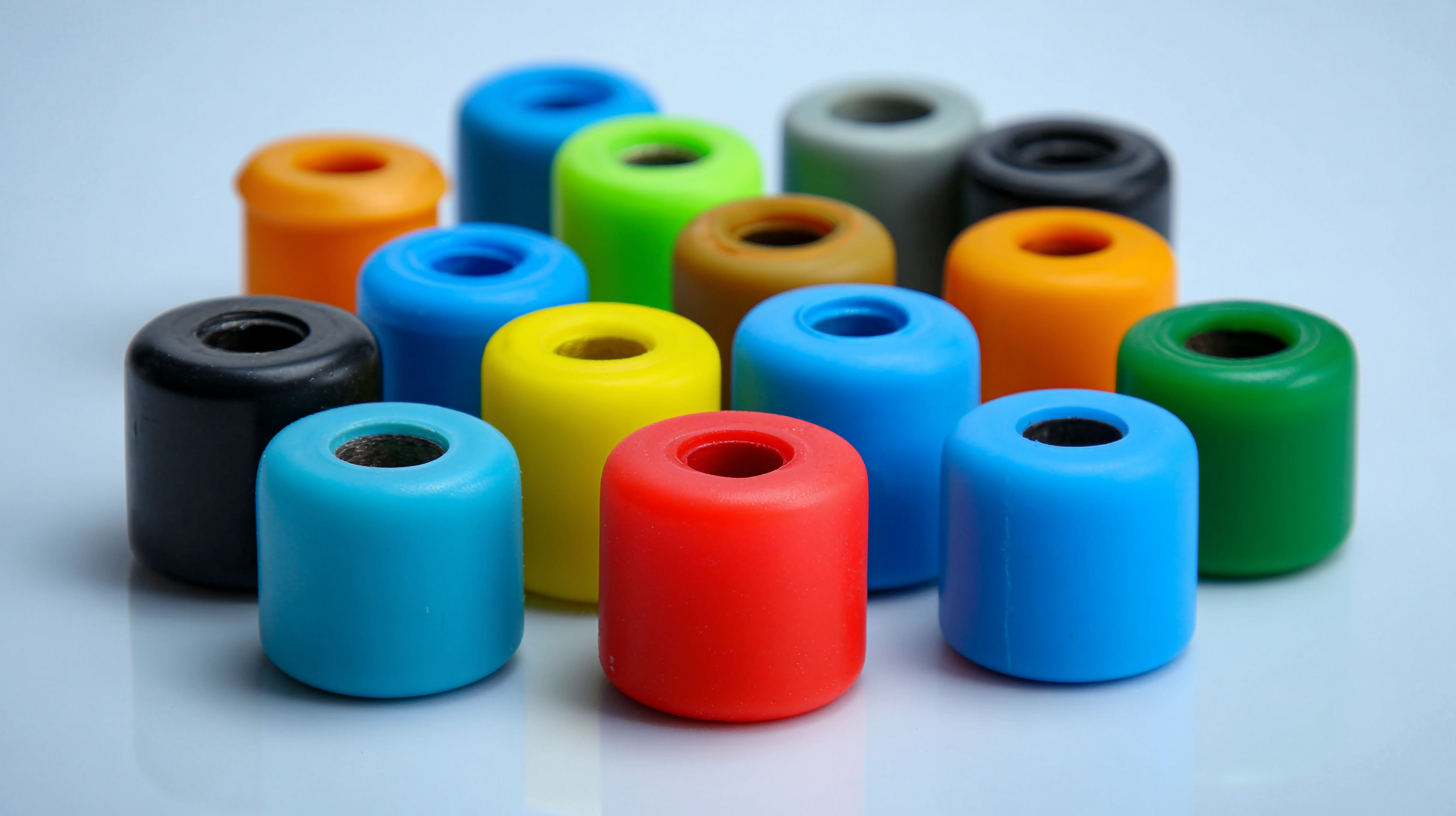

Silicone rubber insulators offer numerous advantages in electrical applications, making them an increasingly popular choice in modern technology. One of the primary benefits of silicone rubber is its excellent thermal stability, which allows it to function effectively in a wide range of temperatures without degrading. This reliability ensures consistent performance in both high and low-temperature environments, essential for applications such as power transmission and distribution.
Furthermore, silicone rubber demonstrates remarkable electrical insulation properties, exhibiting high dielectric strength and resistance to electrical breakdown. This characteristic minimizes the risk of short circuits and enhances overall safety in electrical systems. Additionally, silicone's inherent hydrophobic properties help prevent moisture absorption, reducing the likelihood of mold and mildew growth, which can compromise the integrity of electrical components. These features make silicone rubber insulators not just advantageous but indispensable in ensuring the longevity and safety of modern electrical infrastructures.
Silicone rubber insulators are increasingly recognized for their unique properties, which make them ideal for various modern technology applications. Their excellent thermal stability allows them to maintain performance in extreme temperature conditions, ranging from -55°C to 300°C. This ensures that devices remain functional and reliable, even in harsh environments. Moreover, silicone rubber exhibits outstanding electrical insulation capabilities, which minimizes the risk of electrical failures and enhances safety across different sectors, including electronics and power transmission.
**Tips**: When selecting silicone rubber insulators for your projects, consider the specific temperature range and electrical demands of your application to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, verifying the compatibility of silicone rubber with other materials in your design can prevent potential degradation and improve overall durability.
Another significant property of silicone rubber is its resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, ozone, and moisture. This resistance prolongs the lifespan of insulators, making them a cost-effective choice for industries that rely on long-lasting components. Furthermore, the flexibility of silicone rubber allows for easy molding into complex shapes, enhancing design versatility in various applications.
**Tips**: Always evaluate the environmental conditions where the insulator will be used. Choosing the right formulation can further boost performance against specific weather-related factors, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs.
This chart showcases key properties of silicone rubber insulators that enhance their performance across various technology applications. The properties measured include Temperature Resistance, Electrical Insulation, Chemical Stability, and Mechanical Strength.
Silicone rubber insulators have emerged as crucial components in a variety of modern technology applications, reflecting their diverse industrial uses. Their inherent properties such as high thermal stability, excellent electrical insulation, and flexibility make them ideal for use in environments where extreme temperatures and harsh conditions prevail. For instance, in the automotive industry, silicone rubber insulators are commonly used in electrical systems to prevent short circuits and enhance the overall safety of vehicles.
In the electronics sector, silicone rubber insulators serve a key role in protecting sensitive components from moisture and contamination. Their ability to withstand UV radiation and ozone exposure further enhances their functionality in outdoor applications, such as telecommunications equipment and solar panel installations. Additionally, silicone rubber's versatility allows for customization in shape and size, catering to specific requirements across various sectors including aerospace, healthcare, and consumer electronics. This adaptability underlines the essential role silicone rubber insulators play in advancing modern technology.
 Silicone rubber insulators have emerged as a formidable alternative to traditional insulating materials, such as glass and ceramic, particularly in demanding environments. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, silicone rubber exhibits superior thermal stability, maintaining its performance in temperatures ranging from -60°C to 200°C. In contrast, conventional materials can suffer from degradation, leading to potential failures in high-temperature applications. This resilience makes silicone rubber particularly valuable in sectors like telecommunications and renewable energy, where equipment must endure extreme weather conditions.
Silicone rubber insulators have emerged as a formidable alternative to traditional insulating materials, such as glass and ceramic, particularly in demanding environments. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, silicone rubber exhibits superior thermal stability, maintaining its performance in temperatures ranging from -60°C to 200°C. In contrast, conventional materials can suffer from degradation, leading to potential failures in high-temperature applications. This resilience makes silicone rubber particularly valuable in sectors like telecommunications and renewable energy, where equipment must endure extreme weather conditions.
Moreover, silicone rubber's hydrophobic properties significantly enhance its insulative performance in wet and humid environments. A study by the Electric Power Research Institute highlights that silicone insulators can outperform ceramic insulators by up to 30% in terms of leakage current performance under wet conditions. Additionally, the lightweight nature of silicone rubber reduces installation costs and enhances safety during handling, further solidifying its position in modern technology applications. As industries increasingly seek materials that not only perform under pressure but also offer longevity and reliability, silicone rubber insulators continue to redefine traditional standards in insulating materials.
Silicone rubber insulators are increasingly recognized for their adaptability in various modern technology applications, notably in the electrical and electronics industry. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the silicone rubber market is expected to grow from $10.2 billion in 2021 to $17.1 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 10.5%. This surge is fueled by innovations in silicone formulations that enhance durability and resistance to extreme environmental conditions, making them suitable for use in high-voltage systems and renewable energy infrastructures.
Looking ahead, the future of silicone rubber insulator technology appears promising with ongoing research and development efforts focused on increasing energy efficiency and sustainability. One notable innovation is the introduction of nanocomposite silicone rubber, which incorporates nanoparticles to improve thermal stability and electrical properties. The International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biosources outlines that such advancements could lead to insulators that not only provide better performance but also reduce material consumption by 20-30%, aligning with global sustainability goals. As industries strive to meet stringent regulatory standards, the versatility and performance enhancements of silicone rubber insulators will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping modern technology applications.
| Application Area | Key Features | Advantages | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Industry | High thermal stability, weather resistance | Enhanced durability, reduced maintenance costs | Integration with electric vehicle technologies |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Improved safety and efficiency in power distribution | Smart grids and renewable energy applications |
| Consumer Electronics | Flexible, lightweight design | Portability and convenience | Advancements in miniaturization |
| Medical Devices | Biocompatibility, easy to sterilize | Reduced risk of infection | Growth in wearable health technology |
| Construction | Resistance to UV light and moisture | Long-term reliability in harsh environments | Increasing use in smart building technologies |