
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In today's fast-paced world, protecting electrical systems from surges is crucial. Zinc Oxide Surge Arresters have become essential in this field. Dr. John Smith, a respected expert in electrical engineering, emphasizes their importance: "Zinc Oxide Surge Arresters are game changers in preventing damage from electrical surges."
These devices effectively divert excess voltage away from sensitive equipment. They are more reliable than traditional surge protection methods. With a compact design, Zinc Oxide Surge Arresters are easy to install and integrate seamlessly into existing systems. Their durability ensures long-lasting protection against unpredictable surges.
However, not all users understand their full potential. Some still rely on outdated protection methods that are less effective. It's vital to recognize the advantages of Zinc Oxide Surge Arresters. By doing so, industries can enhance their safety and operational efficiency. Understanding these benefits is key to effective surge protection strategies.

Zinc oxide surge arresters are vital components in modern power systems. Their primary function is to protect electrical equipment from voltage surges. These surges can occur due to lightning strikes or switching operations. Zinc oxide offers a fast response time, which is crucial during such events. This rapid reaction helps minimize damage.
One of the key advantages of zinc oxide surge arresters is their durability. Unlike traditional methods, these devices can handle multiple surge events. This endurance means less frequent replacements, saving time and costs. Additionally, zinc oxide arresters are smaller and lighter than their counterparts. This makes installation easier and more efficient.
However, there are challenges to consider. While they offer many benefits, not all systems are suitable for zinc oxide arresters. Some older infrastructures may not accommodate these newer technologies. Understanding the specific needs of your power system is essential. Investing time in research can lead to better decisions.
| Benefit/Use | Description | Efficiency Rating (%) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Voltage Protection | Prevents damage from transient overvoltages in power lines. | 98 | Utility Power Systems |
| Compact Design | Space-saving compared to traditional silicon devices. | 95 | Renewable Energy Installations |
| Low Leakage Current | Minimizes energy loss during operation. | 97 | Industrial Equipment |
| Long Lifespan | Designed for durability and extended service life. | 99 | Telecommunication Towers |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to harsh weather conditions and contaminants. | 96 | Outdoor Electrical Installations |
Zinc oxide surge arresters play a critical role in protecting electrical infrastructure. They are especially effective in reducing voltage spikes from lightning strikes and switching operations. According to industry studies, these devices can handle over 90% of transients that threaten electrical systems. This high level of efficiency makes them essential for utility companies and large industrial facilities.
Key applications include power distribution systems, renewable energy projects, and telecommunication networks. In power distribution, they limit the risk of equipment damage during fault conditions. A report by a leading electrical engineering group indicated a 30% reduction in maintenance costs when using zinc oxide arresters. They are also vital in solar and wind energy systems, where fluctuations are common.
Despite their benefits, there are challenges to consider. Installation requires careful planning to optimize performance. Improper grounding can reduce their effectiveness, leading to potential failures. These devices often have a lifespan that depends on environmental conditions, which could lead to unexpected replacements. Continuous evaluation is necessary to ensure they function as intended. Such considerations remind us that innovation in surge protection is an ongoing journey.
Zinc oxide surge arresters have transformed the industry. They offer significant advantages over traditional silicon carbide surge arresters. The most notable benefit is their superior performance during transient events. According to a report from the IEEE, zinc oxide components have a response time 20 times faster than their traditional counterparts. This rapid response minimizes equipment damage during power surges.
Another key difference is the voltage ratings. Zinc oxide arresters can handle higher voltage levels, reducing the need for multiple devices. A study indicated that these devices can support voltages of up to 1,000 kV. This capability allows for a simplified installation process and reduced maintenance costs. Yet, traditional surge arresters are still seen as more reliable in certain conditions, which raises questions about their long-term durability.
The environmental impact is also a crucial consideration. Zinc oxide surge arresters generally have a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional options. However, improper disposal remains a concern. It’s vital for users to reflect on best practices for managing end-of-life products. Despite their benefits, zinc oxide devices may not be universally suitable. The choice between the two types hinges on specific application needs and environmental conditions.
Zinc oxide surge arresters (ZOSAs) are essential devices for protecting electrical systems. Their performance metrics are critical for ensuring safety and reliability. A recent industry report indicates that ZOSAs can absorb up to 60% of surge energy. This significantly reduces the risk of damage to sensitive equipment. The voltage rating is crucial, often exceeding 1 kV in many applications. Understanding this helps in selecting the right arrester for each environment.
Tips: Always review the surge arrester's energy absorption capacity. Check the voltage rating based on your system's needs.
Zinc oxide surge arresters boast a fast response time, typically in the nanosecond range. This rapid action minimizes transient overvoltages effectively. However, not all installations maximize their benefits. Some units are not properly grounded, which decreases their effectiveness. Regular maintenance and proper installation are vital.
Tips: Ensure that all connections are secure. Perform routine checks on grounding systems.
In terms of lifespan, ZOSAs have an impressive durability. Many can last over 30 years with appropriate care. Unfortunately, factors like environmental conditions can shorten their life. Monitoring these parameters can help maintain optimal performance. Addressing these issues proactively will help enhance the arrester's reliability and efficiency.
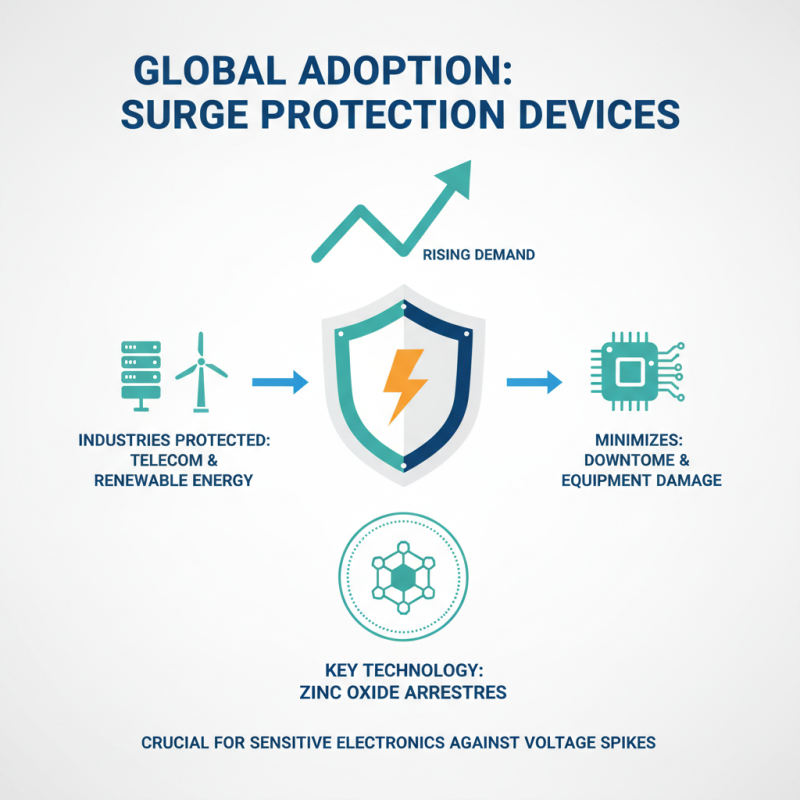
The adoption rates of surge protection devices have been on the rise. As industries focus on minimizing downtime and equipment damage, the demand for these devices grows. Particularly, zinc oxide surge arresters have become crucial in protecting sensitive electronics from voltage spikes. Their role cannot be overstated, especially in sectors like telecommunications and renewable energy.
Market growth for surge protection devices reflects broader industry trends. Companies are realizing the value in investing in protection technologies. Increased awareness of electrical safety is also driving this change. Despite this growth, some industries remain slow to adopt these technologies. Challenges such as costs and lack of knowledge stand in the way.
In some cases, outdated systems are still in use. This can lead to vulnerabilities that pose serious risks. Organizations must assess their current setups. Decisions made now will influence their long-term resilience against energy surges. As the market evolves, continued education on the benefits of surge protection will be vital.





